Soft robotics is a promising field with the potential to transform various industries, from healthcare to manufacturing. By mimicking human-like movements, soft robots can interact more safely and effectively with humans and their environments. The Soft Wrist Exosuit, in particular, can assist with rehabilitation and improve worker safety in industrial settings.
This soft robotics application focuses on achieving precise control over the air pressure in each fabric pneumatic artificial muscle (fPAM). The fPAMs require accurate and timely pressure regulation to ensure safe, smooth and controlled movements. Additionally, the system must be able to handle varying flow demands as the exosuit performs different tasks.
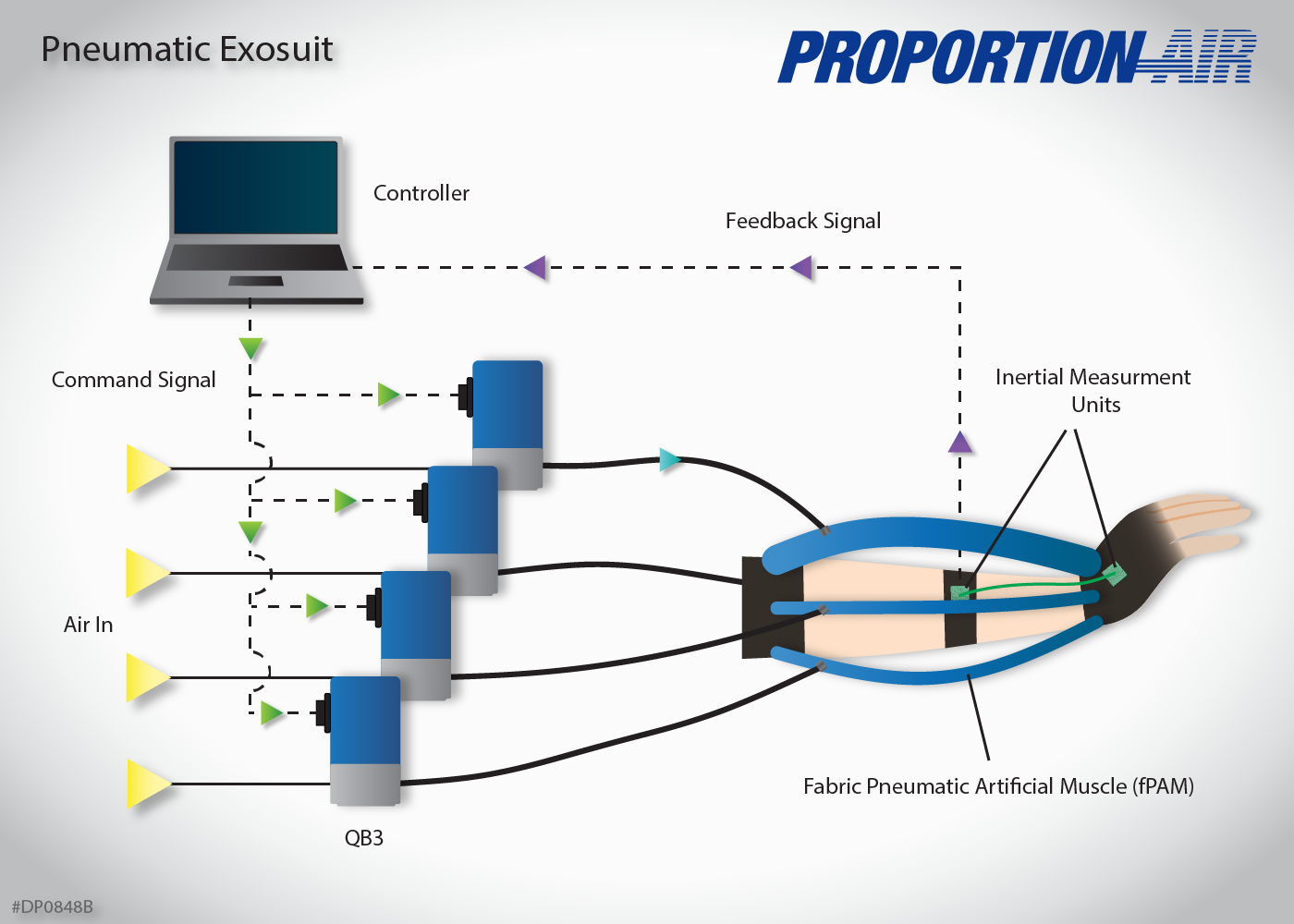
In this drawing, four QB3s are attached to the four fPAMs of the Soft Wrist Exosuit to assist movement. The controller sends a signal to the QB3 units to inflate the corresponding fPAM(s) responsible for causing the wrist flexion/extension and ulnar/radial deviation needed. (The drawing shows the flexion of the wrist caused by the dorsal fPAM being inflated.) The inertial measurement units (IMUs) relay the angle of the wrist back to the controller to ensure the exosuit is operating properly.
